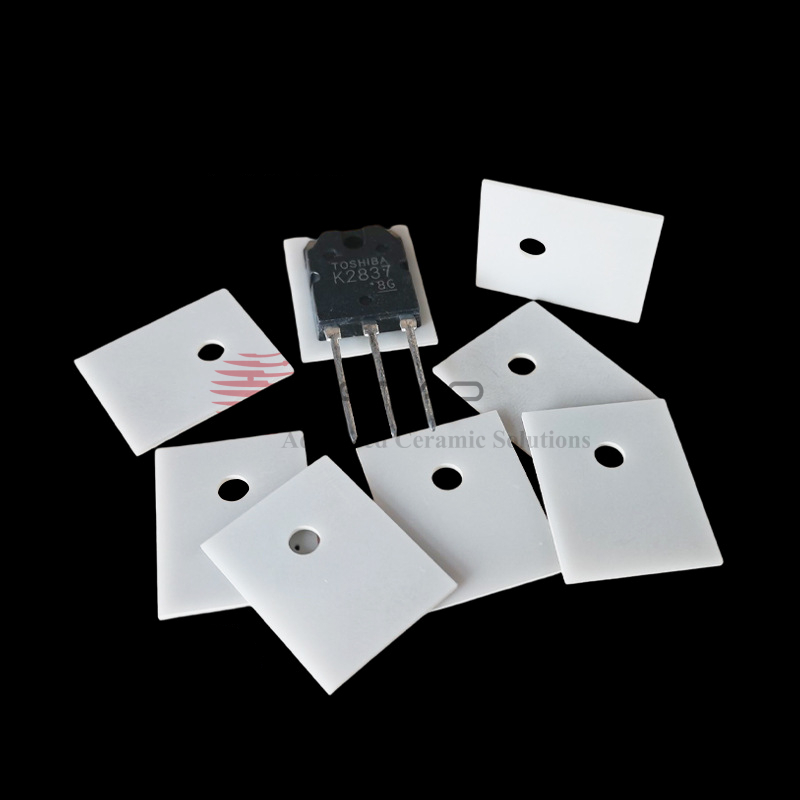
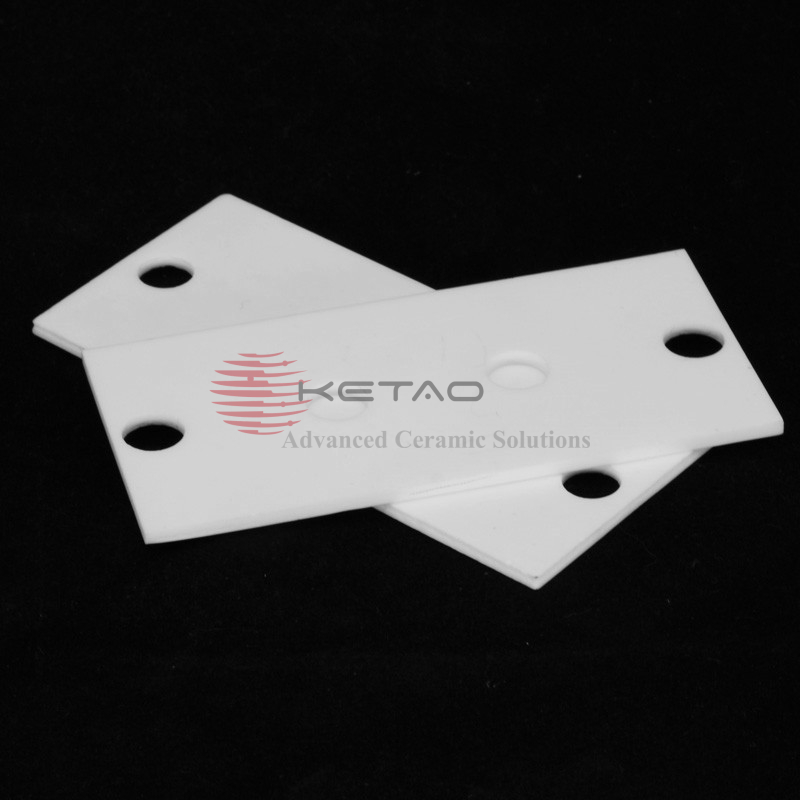
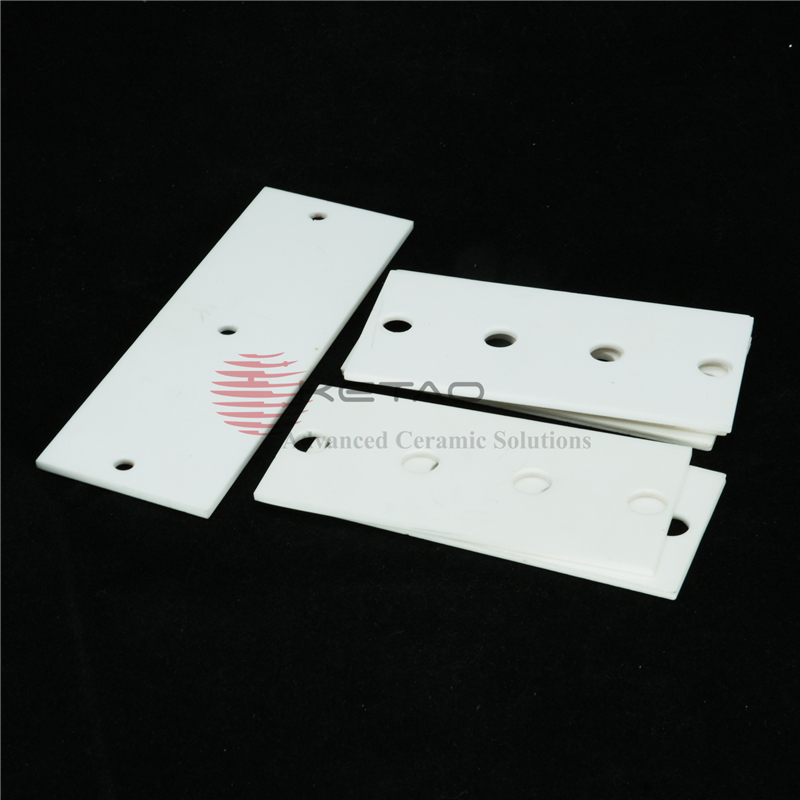
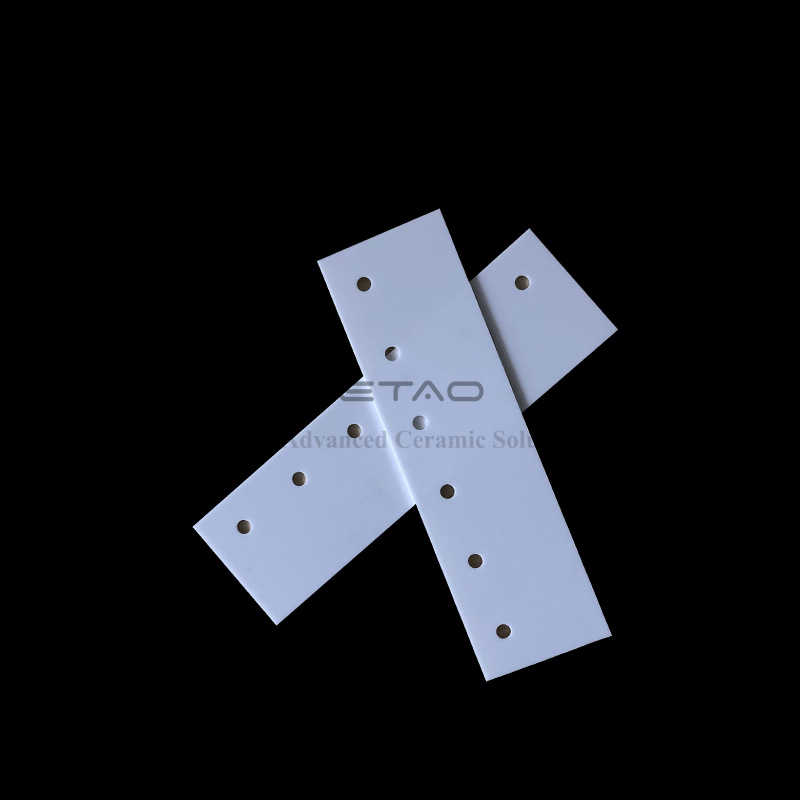
96 Alumina Ceramic Substrate for LED Insulation plate
Alumina ceramic substrates are thin, flat plates made from high-purity alumina materials that are used as a base or support for electronic components. They are commonly used in electronic devices such as sensors, microelectronics, and other applications where thermal and electrical conductivity, high strength, and chemical stability are required.
Alumina ceramic substrates offer several advantages, including high thermal conductivity, excellent mechanical strength and hardness, chemical stability, and resistance to wear and abrasion. These properties make them ideal for use in harsh environments where electronic components need to function reliably.